According to Prof. Neil H. Borden, " The marketing mix refers to the apportionment of efforts, the combination, the designing and the integration of the elements of marketing into programme or mix which, in the basis of an appraisal of the market forces will best achieve the objectives of an enterprise at a given time. Thus, the marketing mix is an integration of marketing elements.
learn about insurance, insurance types i.e. fire insurance, Auto insurance, life insurance..insurance policy, importances of insurance, marketing, history of insurance and its business in Nepal, Scope of insurance, insurance companies in Nepal
Sunday, August 30, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING MIX
According to Prof. Neil H. Borden, " The marketing mix refers to the apportionment of efforts, the combination, the designing and the integration of the elements of marketing into programme or mix which, in the basis of an appraisal of the market forces will best achieve the objectives of an enterprise at a given time. Thus, the marketing mix is an integration of marketing elements.
OBJECTIVES OF LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING
- Spread of life insurance message
- Mobilization of savings in the form of pension
- Profit maximization
- Successful distribution of life insurance products
- Improving customer services
- Increasing customer base and its spread
- Developing corporate image
- Developing guiding policies and their implementation for a good result
- Suggest solution by studying the problems relating to life insurance business.
MARKETING OF LIFE INSURANCE
In LIC, life insurance service are rendered with a view to protect the people against the risk of loss due to accident, fire, death, sickness, unemployment and so on.
Some people might argue that there is service marketing, but only marketing in which the service element is greater than the product element. We do agree that, in the sale of majority of the goods, there are both a product part as well as a service part. However, there are so many service organizations like insurance companies, banks, transport companies who do not think of themselves as marketers of goods. They see themselves as providers of services.
Definition of Services
The term service has been differently defined by different authors. According to Ivanovic, "Service is the work of dealling with customers, or payment for the work, services are benefit which are sold to customers or clients such as insurance, transport and educationa". According to Philip Kotler, " A service is an activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Its production may or nay not be tied to a physical product".
Characteristics of Life Insurance Services
Life insurance services, as described above, have a number unique characteristics that place them in separate category compared to physical goods. These characteristics create special marketing challenges. They are given below :
1. Intangibility : Llife insurance services are intangible in nature. It is quite different fromm other commercial products. The consumer has to have faith in the services of life insurance provider. Services are intangible and therefore, cannot be seen, felt or tasted. The customer has to be encouraged, enthused and helped to visualize the unforeseen tomorrow and usefulness of a life insurance products. Unlike tangible products, there are no factories and production lines for life insurance.
2. Heterogeneity : Life insurance services are heterogeneous in their nature. That is, they are highly variable. Each life insurance product of the service i some what different from other products of the same services. Different kinds of insurance products are developed from time to time to cater to the specific needs of customers.
3. Inseparability : Very often services cannot be separated from their provider. It is very important to understand the heart and soul relationship between product and service, cost and quality. Life insurance products continues to exist over a long period of time, and for making its service available, the insured person has to go on paying the purchase price (premium) through out the term of the policy. This ensures that the benefits already accrued under sale are not lost. Hence due to inseparability, direct sale of services, is the only channel of distribution. In LIC, insurance agents represent and help in promoting inseparable services.
4. Changing Demand : The success of life insurance service marketing in turn depends on the ability of the firm to find a customer and to satisfy his wants. For this purpose instead of trying to sell what can be produced the business firm should produce what is really needed by the customer and what would satisfy his wants. It is a buyer's market, by and large, the seller i.e. the LIC has to take decision whether to sell a particular policy to particular person or not on the basis of information disclosed by the buyer himself in the proposed form.
Friday, August 21, 2009
KINDS OF LIFE INSURANCE POLICIES
Different insurance company can introduce different kinds of life insurance policies. Some of them are classified in to the following kinds.
1. Whole life policy
The whole life policy will mature only on the death of the insured. This kind of policy is done to protect the dependents of insured in which low premium is paid up to his life. Although, this type of policy has no financial gain to insured, reach persons prefer to take this kind of policy to make provision for the payment of death duty. The policy can further be classified as under.
- Ordinary whole life policy : Under the ordinary whole life policy premiums are payable throughout the life of the insured and the insured sum is payable to his dependents or nominee only after his death.
- Limited premium whole life policy : Under the limited premium whole life policy, the premium is paid for a limited or selected period (say up to 20 years) but the policy will mature for payment only on the death of the insured.
- Single premium whole life policy : Under this policy, the insured is liable to pay the total premium once in a life but the insured sum is payable to his dependents only after his death.
- Convertible whole life policy: The convertible whole life policy gives the option to the insured for conversion into endowment policy after the expiry of five years of the policy.
2. Endowment policy
Endowment policy is issued for a fixed period and the premium is payable during that period only. The insured sum is payable to policy holder after the expiry of the period or to his nominee on his death which ever is earlier. This type of policy is most popular because it provides financial security on old age sufferings. The following are the different types of endowment policies.
- Ordinary Endowment policy : The ordinary endowment policy will mature for payment on the survival of the date or his death within the endowment policy which ever is earlier.
- Pure Endowment policy: The pure endowment policy will mature for payment, only if the insured person survives up to the endowment period otherwise the insured sum is not payable by the insurance company.
- Double Endowment policy : Under this policy, if the insured survives up to the endowment period, he will get double the sum insured or only the insured sum is payable on his death within the endowment period.
- Anticipated Endowment policy : Under this policy, a part of sum insured is paid at certain intervals during the endowment period and the balance of insured sum is paid at maturity period.
- Deferred Endowment policy : Under this policy, after the expiry of specified period, the insured sum is payable to insured person or nominee. The sum is payable only after the end of specified time, so there is no major factor of when the insured died.
- Joint life Endowment policy : This policy is taken on the life of two or more persons and will mature for payment on the expiry of the endowment period or on the death of any one of the life insured before the endowment period.
3. Term insurance policy
The term insurance policy is used for short term ranging from one year to specified number of years and will nature for payment only on the death of insured within the period, but if he survives, nothing is payable. Following are the types.
- Ordinary term policy : The ordinary term policy is used for very short period of years and the premium is generally paid in one installment called the straight premium. The insured sum is payable only if death occurs within the term.
- Decreasing term policy : This policy is issued to the borrowers of money and the amount of policy payable at the end of each year is automatically reduced and equal to the outstanding loan which will be paid if the insured dies before the end of term.
- Renewal term policy : This policy can be renewed after the expiry of the term without medical examination but a different rate of premium is applicable to the age at the time of renewed.
There are other life policies also. Some of there are as follows:
- Multi purpose life insurance policy which provides several benefit under one insurance contract, such benefits are old age benefits, regular income maintenance, children education, cost benefit, marriage cost benefit etc.
- Employee life insurance which is taken by the employer to provide security and safety of employee for better performance and productivity.
Thursday, August 20, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE POLICY
 Insurance is a transfer of risk. Life insurance policy means a written document which says a payment of money is made on death but not one which says payment is made only if the death is accidental or if death happens in certain circumstances or during the period a person has agreed to pay premiums. A life insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an individual and insurer (insurance company) in which the individual transfers some or all of his or her human life value to the insurance company.
Insurance is a transfer of risk. Life insurance policy means a written document which says a payment of money is made on death but not one which says payment is made only if the death is accidental or if death happens in certain circumstances or during the period a person has agreed to pay premiums. A life insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an individual and insurer (insurance company) in which the individual transfers some or all of his or her human life value to the insurance company.Trying to purchase the best life insurance policies can be confusing. Since each person's situation is different, careful research will help in making the right decision.
Different insurance company can introduce different kinds of life insurance policies. The choice between whole of life insurance policies, term life insurance or any of the other options available is not about which one is better or worse than the other. Each has its place. By doing a proper financial needs analysis, life insurance applicants will have a far more accurate idea of exactly how much life insurance to purchase, in what areas and how much they can afford to spend. Another option is to mix and match the various options to better fit in with one's needs.
In simplest definition, a life insurance policy, for which premium payments have been paid as agreed upon according to the terms of the contract, pays out to your beneficiary upon your death the value of the policy. From your viewpoint, the biggest advantage to carrying a life insurance policy is peace of mind knowing that in case of your untimely demise, your nearest and dearest will be clothed, shod, fed and educated so they can make their way in an uncertain world with at least a minimal financial buffer to protect them. From their viewpoint, in your absence, they will have the means to make any necessary adjustments with somewhat less misery than if they would if not provided for.
Wednesday, August 19, 2009
PROCEDURES OF EFFECTING LIFE INSURANCE
1. Submit the proposal form
The interested person can obtain the proposal form from the agent or insurance company. The person is requested to answer all the questions in the proposal form and give accurate and adequate information on all the material items. By this duly filled proposal form i.e. printed questionnaire paper, insurer receives detail information of the person such as name, address, occupation, date of birth, mode of payment etc.
2. Submit certificate of age
The proposer has to mention the exact date of birth in the proposal. The risk of life insurance depends on age and the rate of premium is fixed according to it. For this purpose, proposer is obliged to submit any one of birth certificate, citizenship certificate, horoscope, school certificate.
3. Medical examination
On the receipts of proposal along with birth certificate, the insurance company arranges a medical, examination of the interested person by one approved doctor on its official. Normally the medical examination is out of charge which helps to ascertain the risk of life.
4. Submission of Agents report
If the proposer came from an agent, it is the responsibility of agent to submit the report of proposer in prescribed manner including proposer’s character, health, financial position and other information.
5. Scrutiny of repots
The proposal form, filled by proposer, report of medical examination and report of agent are examined by an expertise team of life insurance company to decide whether the proposal is acceptable or not.
6. Acceptance of proposal
When the scrutiny is in favour of insurance and all the submitted documents are favourable, the insurance company accepts the proposal. If the proposal is accepted the insurance company communicates the acceptance to the insured and demands the first premium.
7. Payment of first premium
On the receipts of communication of acceptance and demand of first premium the proposer should submit the first premium. If the first premium is paid, the insurance comes in to operation and risk is converted to insurer.
8. Issue of insurance policy
At last, a formal document called the life insurance policy is prepared. It should be sealed, singed and stamped deed or contract of life insurance describing all the terms and conditions, rules and regulations of life insurance contract. This policy is sent to the insured through registered post or other means of Nepal.
Tuesday, August 18, 2009
FEATURES OF LIFE INSURANCE
 1. General contract
1. General contract2. Investments
Insurer is liable to return premium along with some benefit to the insured person after the expire of time or the death of insured person. Thus premium paid by him regularly is like depositing money in a bank. In case of his premature death the fixed amount is paid to his nominee.
3. Conditional contract
Life Insurance is a conditional contract because the insurer shall pay the insured sum only when the contract is continuing by payment of premium. In addition, the insurer promise to pay the sum is also conditional upon the satisfactory proof of death and other condition as mentioned in the policy.
4. Assignment and nomination
Life insurance can be assigned freely for legal consideration, love or affection. The assignment shall be complete and effective only in accordance on the policy mention itself or by a separate deed. Life insurance policy holder can nominate a person or person to whom the money secured by the policy shall be paid in the event of his death. In case if nominee dies, the sum shall be paid to the policy holder or his legal representations.

5. Insurable interest
Life insurance must have insurable interest means monetary gain from the continuation of life or loss from its destruction. Although the loss of the insured cannot be measured in terms of money. But in practice certain sum of money, sometimes a bonus is fixed to be paid.
6. Utmost good faith
The life insurance requires the doctrine of utmost good faith. In life insurance, both the party insured and insurer should supply all the material facts to each other which help to ascertain the risk. Both the party has duty and responsibility to make full and true disclosure of all the material facts to the risk which can influence the decision of proposer whether to apply or not to apply for insurance.
Monday, August 17, 2009
TYPES OF LIFE INSURANCE
Term life insurance is the simplest form of life insurance. It is also the most inexpensive. It covers you for a specific term. During this period of time, your premiums do not change.
Like all life insurance, term life insurance is an agreement between you and the life insurance company. You agree to pay a predetermined premium rate. Your life insurance company agrees to pay a sum to your beneficiary if you die—as long as you were still paying your premiums at the time of your death.
With term life insurance, coverage pays off if needed during a specific time period. Term life insurance provides protection for a specific period of time - like 20 years. Because it does not accumulate cash value, Term insurance is inexpensive when compared to Whole life insurance (Permanent insurance.) Term life insurance is in low initial premiums provide greater coverage for the money & good for covering large loans such as auto loans or mortgages loans.
2. W
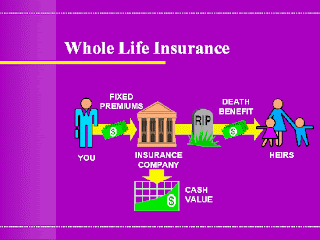 hole Life Insurance
hole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is purchased as a long-term policy that may serve as not only an insurance policy but depending on type, as an investment vehicle as well.The whole life insurance will mature only on the death of the insured. This type of insurance is done to protect the dependents of insured in which low premium is paid up to his life. Although, this type of insurance has no financial gain to insured, reach persons prefer to take this type of insurance to make provision for the payment of death duty.
Whole life insurance, like term, is exactly what it sounds like. A policy without company specific modifications will have a level premium and level face value for your entire life. Unlike Term, however, whole life builds a cash value which you can claim if, in later years, you decide that you no longer need the life insurance.
3. Universal Life Insurance
 Universal life insurance is a type of life insurance that builds a savings plan out of which your premium is paid. Universal life insurance is flexible combination of Term life insurance and Whole life insurance, so it is commonly known as 'flexible' life insurance because you can change the premium or face value, although it usually has to prove insurability if you want to increase the face value. The interest it accumulates can also fluctuate with the economy. So if you start with an unusually high interest, you may find it necessary in future years to increase your premium slightly to keep the policy in force.
Universal life insurance is a type of life insurance that builds a savings plan out of which your premium is paid. Universal life insurance is flexible combination of Term life insurance and Whole life insurance, so it is commonly known as 'flexible' life insurance because you can change the premium or face value, although it usually has to prove insurability if you want to increase the face value. The interest it accumulates can also fluctuate with the economy. So if you start with an unusually high interest, you may find it necessary in future years to increase your premium slightly to keep the policy in force.
It has many of the features and minimal premiums of a term policy, and yet offers flexibility to increase those premium payments and accumulate equity using some of the features and advantages of a whole life policy.
Sunday, August 16, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE

Life insurance is designed to cover the final expenses, including funeral expenses and bills, of the policyholder upon his death. Life Insurance can also provide a means for a policyholder to provide for his heirs financially. Life insurance is issued either as a term policy, which
 does not build equity but which generally has lower premiums, and whole life insurance, which does provide equity the policy holder can borrow against. Whole life policy premiums are generally more expensive than term insurance. For most people, the purpose of life insurance should be to replace the financial contribution made by a family member. Life insurance can be pure insurance, which pays only on the death of the insured, or cash value insurance, which also has a savings vehicle. Most people who need life insurance are better off with pure insurance and saving for retirement through other vehicles. Proceeds from life insurance cover three types of expenses: replacement of the policyholder's income or work, estate taxes, and burial costs. When you consider the amount of insurance to buy, consider the following:
does not build equity but which generally has lower premiums, and whole life insurance, which does provide equity the policy holder can borrow against. Whole life policy premiums are generally more expensive than term insurance. For most people, the purpose of life insurance should be to replace the financial contribution made by a family member. Life insurance can be pure insurance, which pays only on the death of the insured, or cash value insurance, which also has a savings vehicle. Most people who need life insurance are better off with pure insurance and saving for retirement through other vehicles. Proceeds from life insurance cover three types of expenses: replacement of the policyholder's income or work, estate taxes, and burial costs. When you consider the amount of insurance to buy, consider the following: 1. Most of the life insurance should be on a family member whose salary is important to the family budget.
2. Consider a relatively small life insurance policy on a stay-at-home parent to cover child care and other expenses.
3. Don't buy life insurance on children. Instead, buy life insurance on other family members for the benefit of children.
4. Consider reducing the amount of life insurance you have as you build more financial assets.
5. Pass on credit life insurance and mortgage life insurance if you can. These plans are restrictive and expensive. Buy more general life insurance instead if you feel a need.
6. Pass on life insurance altogether if you are single and don't have anyone depending on you. At most, get a small policy to spare your family burial expenses. You should buy about 12 times the amount of money you would need annually to replace what the family member is contributing. For example, if you would need $50,000 a year to replace the death of an employed member, you would need a $600,000 policy.
INSURANCE DOCUMENTS
 There are various insurance documents used for different types of insurance, which are essential for all classes of insurance business. The object of insurance documents is give to the insurer full particulars of the risk against which insurance protection is desired. It also provides evidence of contract into which the parties have entered.
There are various insurance documents used for different types of insurance, which are essential for all classes of insurance business. The object of insurance documents is give to the insurer full particulars of the risk against which insurance protection is desired. It also provides evidence of contract into which the parties have entered.1. Proposal Forms
The company's printed proposal form is normally used for making an application for the required insurance cover. The proposal form contains questions designed to elicit all material information about the particular risk proposed for insurance. The number and nature of questions vary according to the particular class of insurance covered.
In Marine Cargo Insurance, Insurance document is not the practice to use a proposal form, although sometimes it is usual to obtain a questionnaire or a declaration form duly completed. Proposal forms are used for hull insurance.
In Fire Insurance, the practice varies among the companies, proposal forms are not generally used for large industrial risks where inspection of the risk is arranged before acceptance of the risk. Forms are used for simple risks. Proposal forms are used in respect of risks which are normally declined but have to be accommodated to retain the goodwill of the client.
In Miscellaneous Insurance, proposal forms are invariably required and they incorporate a declaration which extends the common law duty of good faith. Fire proposal forms may or may not have the declarations. The following items may be considered as common to all proposal forms.
- Proposer's name in full
- Proposer's address
- Proposer's profession, occupation or business
- Previous and present insurance
- Loss experience
- Sum insured
- Other Section's - Signature, date, place etc.
Policy forms, like proposal forms, vary within wide limits as between different classes of insurance but they have certain features in common. The policy is a document which provides evidence of the contact of insurance. This document has to be stamped in accordance with provisions of the Indian Stamp Act 1899. Where the insurance is governed by a Tariff or a Market agreement, the policy wording is prescribed therein itself and it is obligatory for insurers to use these wordings. In fire and miscellaneous insurance, the policy form used is on a scheduled basis i.e. all individual details relating to a particular insurance are grouped together in a schedule. Generally speaking policies are divisible into certain well defined sections and these are as follows:
- Recital Clause or Preamble
- Operative Clause
- Attestation Clause
- Conditions
- Schedule
A cover note is a document issued in advance of the policy. It is issued when the policy cannot for some reason or the other, be issued straight away. Cover notes are issued when the negotiations for insurance are in progress and it is necessary to provide cover on a provisional basis or when the premises are being inspected for determining the actual rate applicable. Pending the preparation of the policy, the cover note is issued as evidence of protection for a temporary period of time and to prove that cover is in force. Here is a brief detail of cover.
In Marine Insurance, marine cover notes are normally issued when details required for the issue of policy such as name of the steamer, number of packages or exact value etc are not known. In Fire Insurance,, the operative clause of a fire cover note is issued in consideration of the proposer named in the schedule having proposed the effect of an insurance against fire for the period mentioned, on the usual terms and conditions of the company's policy. In Motor Vehicle Insurance, motor cover notes are to be issued in the form prescribed by the Motor Tariff.
4. Certificate of Insurance
In motor insurance, in addition to the policy, a certificate of insurance is required by the Motor Vehicle Act. 1988. This certificate provides evidence of insurance to the Police and Registration authorities. It contains the essential features of the cover including the terms and conditions. In Marine Insurance, certificate of insurance is issued to provide evidence of cover on shipments insured under cargo open cover or floating policies.
5. Endorsements
It is the practice of insurers to issue policies is a standard form, covering certain perils and excluding certain others. If it is intended, at the time of issuing the policy to modify the terms and conditions of the policy, it is done by setting out the alteration ia a memorandum which is attached to the policy and forms part of it. The memorandum is called an endorsement.
Saturday, August 15, 2009
DEFINITION OF INSURANCE COVERAGE
 Insurance needs are a fact of life in both business and our personal affairs. Nearly everyone in the industrialized world carries some sort of insurance. Many people carry several different types of insurance. In some professions, insurance is a necessity. In cases of a mishap, or even deliberate harm, insurance can mean the difference between getting back on one's feet or never recovering.
Insurance needs are a fact of life in both business and our personal affairs. Nearly everyone in the industrialized world carries some sort of insurance. Many people carry several different types of insurance. In some professions, insurance is a necessity. In cases of a mishap, or even deliberate harm, insurance can mean the difference between getting back on one's feet or never recovering.Health Care
A major form of insurance coverage is health care insurance. Health care insurance covers treatment for illnesses and accidents. Many policies also cover preventative care. Health care coverage is designed to protect individuals against the excessively high costs of paying for treatment out of pocket. It is often covered by employers, but many individuals cover themselves. Medicare and Medicaid are federally issued health care coverage programs. Some states also have health care programs, more often for children. Nonetheless, nearly 46 million Americans had no health insurance coverage at all in 2007, according to the National Coalition on Health Care.
Life Insurance
Life insurance is designed to cover the final expenses, including funeral expenses and bills, of the policyholder upon his death. It can also provide a means for a policyholder to provide for his heirs financially. Life insurance is issued either as a term policy, which does not build equity but which generally has lower premiums, and whole life insurance, which does provide equity the policy holder can borrow against. Whole life policy premiums are generally more expensive than term insurance.
Property Insurance
Property insurance is designed to provide the means to repair or replace items of value in the event of an accident, natural disaster or deliberate acts. Homeowner's insurance, renter's insurance, automobile insurance, flood insurance and insurance for individual items of value such as jewelry or musical instruments are all classified as property insurance.
Business Insurance
Many business owners carry insurance for their commercial enterprises. They may insure their inventory, office facilities or manufacturing equipment. In a partnership the partners may take out insurance policies on one another in the event of the untimely death of one or more of the partners.
Liability Coverage
The most commonly known form of liability coverage is malpractice insurance for physicians, which is nearly universally required as a condition to practice medicine. Many states require drivers to carry automobile insurance as a condition of driving. Some property insurance policies also protect homeowners and apartment dwellers from financial responsibility in the event a visitor suffers an accident or causes damage.
Disability Insurance Coverage
Disability insurance protects the policyholder against the loss of income if he or she becomes unable to work due to illness or injury before reaching retirement age. Disability insurance can be issued as a long term or short term policy.
Friday, August 14, 2009
EVOLUTION OF INSURANCE
 In the history of mankind, the nature of insurance was found in the form of marine trade loans or carrier contracts. Evidence in the record of insurance was made in Babilognia and in India at early period. In the holy book of Hindus. “Rigbeda” the concept of “Yogakshema” is more or less akin to the well being and security of the people. The code of “Manu” had recognized for sharing the future losses.
In the history of mankind, the nature of insurance was found in the form of marine trade loans or carrier contracts. Evidence in the record of insurance was made in Babilognia and in India at early period. In the holy book of Hindus. “Rigbeda” the concept of “Yogakshema” is more or less akin to the well being and security of the people. The code of “Manu” had recognized for sharing the future losses.
In ancient period, international trade was done through sea transit so the risk was attached on both ship and cargo. During that period traders were made an agreement among themselves under which the loss caused to any person was compensated by dividing the loss among themselves, named as “General Average”. At the same time “Battomry Bond” was developed to provide ship loan which will repay with interest, if the ship reaches destination safety. Yahoodies are the main contributor to develop modern marine insurance when they were forced to leave France.
In same country commercial clients such as Venice, Geneva, Florence were started to use the modern Marine polices whereas chamber of insurance was established in Lombard street of England to issue insurance certificate. A father of modern marine insurance, Edward Lloyd published insurance news regularly. Later on Lloyd’s house was turned into center of Marine insurance Business and still now, it is the place of corporation registration and renew.
Life insurance made its first appearance in England on 1653 by William Gybbons. The first life insurance company named ‘The hand in hand society’ was opened in 1696. Life insurance was not popular in United States during the 18th century, because of serious fiactuation in death rate. After 18thIndia, the first life insurance company-Bengal presidency was established in 1818. century, they began to show their interest in this business because of the application of level premium plan. In our neighboring country,
After Marine insurance & life insurance, fire insurance was developed. In the beginning of 16thGermany. Fire insurance was developed in England after the great fire in 1666. About 85% of houses were burned to ashes and property worth near about 10 cores of sterling pound were completely burnt off. Five insurance office was established by 24 members in 1710 is still now very popular and successful.
Thursday, August 13, 2009
PRINCIPLES OF INSURANCE

The fundamental principles of insurance are common in all types of insurance contracts with the exception of the principle of indemnity which is not applicable to life insurance contract. Following principles of insurance are applicable in insurance contracts.
1. Principle of utmost good-faith
All the material, facts and information relating to proposed contract should supplied by each party to others in true and correct manner which helps to enter in to a contract and proves as a legality. Insurer and insured both are under an obligation to disclose relevant material information which may effect the decision of each other. All the insurance contract based upon mutual trust and confidence between the insurers and insured.
Utmost good faith requires each party to tell others “The truth, the whole truth and nothing but the truth”. If at any time, it is found that the insured has closed some material facts, the contract of insurance becomes avoidable at the option of the insurer. Like the same, the insurer must also disclosed the scope, advantage, disadvantage and provision of insurance contract and its all material facts.
2. Principle of insurable interest
All the valid insurance contract must have insurable interest in the object or life insured. Insurable interest is understood as on proprietary or monetary interest in the preservation of things or continuance of life, recognized by law. It follows that one can have an insurable interest only when one should stand to benefit financially by the continence of life or subject insured.
A person is said to have an insurable interest in the property, if he is financially compensated by its loss, destruction or non-existence. Similarly a person taking a life insurance policy must have an insurable interest in the life of the insured person. In case of fire insurance, the insured must have insurable interest in the things insured against fire. Thus, insurable interest means monetary gain from the continuation of subject matter or loss from its destruction.
3. Principle of Indemnity
Indemnity means security against loss or damage or compensation for loss. It is a principle that a person gets exactly the same amount as he has lost due to the loss of his property or things. The compensation can never be more than the amount of actual loss suffered by the insured. In another words, insured is never allowed to make profit out of loss. If the insurance company agree to pay fixed sum higher than the amount of loss which is insured may suffer, there with be a possibility of destroy by intention to make a profit out of insurance.
All contract of insurance, except for life insurance contract are contracts of indemnity. The principle of indemnity cannot applied to life and other kind of personal insurance, because the loss of life i.e. death of a person cannot be calculated in terms of money, nor the money can compensate for loss of life. So in life insurance, a previous agreement regarding the amout payable one the happening of risk is made between insurer and insured.
4. Principle of proximate cause
Proximate cause came from Latin word ‘causa proxima’ which means nearest or immediate cause. This principle is based that the compensation is paid if the cause is insured. If the cause of loss is insured, the insurer will pay, otherwise the insure will not be liable to compensate. According to the principle of proximate cause, if the loss is produced by two or more than two causes acting one by one, it become necessary to choose the most important, effective and efficient, the most powerful and immediate or nearest cause which has brought about the loss. The powerful and immediate or nearest cause which has brought about the loss. The powerful efficient and effective cause is known as proximate cause and all other causes are known as remote cause.
For an example, an insured suffered in an accident and was admitted to the hospital. While undergoing treatment, it is found that he has serious disease which caused his death. According to this principle, the death was the cause of services disease and the accident is not payable under personal accident insurance and the claim is payable under life insurance, if he has insured.
5. Principle of subrogation
The principle of subrogation, also known as ‘Doctrine of rights substitute’ is an extension and outcome of the principle of indemnity. This principle prescribes that the scrap or what ever is left of the damaged subject matter of insurance passed in the hands of insurer after the payment of claim. Thus, subrogation is the transfer of right and remedies of the insured in the subject matter to the insurer after the indemnification. In simple word, after paying the amount of loss to the insured, the insurer gets all the rights which is available to be insured.
6. Principle of contribution
This principle refers to the equitable distribution of loss between different insurer. Sometimes a person insures his goods and property with more than one insurer. This is referred to the double insurance and all these insurer are known as co-insurer. In case of loss, the incurred compensated against the actual amount of loss insured through the risk. In such as case, having co-insurer, they follow the principle of contribution and contribute that proportion of loss which the policy insured. Thus, the insured cannot claim total loss to each insurer. The total loss suffered by the insured in contributed by different insurer in the ration of value of policy issued by them.
7. Principle of Mitigation of loss
Mitigation of loss means to minimize or decrease the loss. It is the duty of the insured to act to minimize the loss. Under this principle, it is prescribed that when over the event of risk, occurs, it shall be the duty of the insured to take all such steps to minimize the loss as would have been taken by any person who is not insured. The idea behind this principle is that the insured should not become careless and inactive in the event of mishap because of property insured. This does not mean that the insured should risk his own life for saving the property which is getting damaged or destroyed.
The principle of mitigation of loss provides a check on the behavior at the time of loss. It implied that the reasonable efforts towards the saving of insured properly must be made by policyholder in the event of loss occurred.
BENEFITS OF INSURANCE
- Risk Transfer : Businessman can easily and conviently transfer the risk of loss of insurance. It also safeguard the interest of individual and public.
- Protection : Businessman do not have to worry about losses or damage when the risk of loss to their property is duly insured. They will receive compensation against actual loss their position becomes "as you were" even though the actual loss takes place. In life insurance , life policy give financial protection to the dependents to the extent of the assured who may be the only bread winner in the family.
- Assured Profit : An insured businessman or policy holders can enjoy normal expected profits eg. 15% or 20% margin of profit.
- Benefits to Consumers: As the property of the businessman is duly insured, and he can get a normal profit margin, he can charge lower prices to consumers.
- Insurance Serves as a Basis of Credit : Insurance has the effect of improving credit standing of businessman, commercial banks and financial institutions insist for insurance of articles which are kept as security for loans. Life policy is a valuable asset and can raise an emergency loan against it.
- Investment : A life insurance contract provides not only protection but also investment, or a pension in old age. Under life policy, one can also get bonuses added to the policy amount when we have with profit life policy.
- Insurance encourages savings : Insurance is particularly true of life insurance. The insured person must save out of his current income an amount equal to the premium to be paid regularly and punctually. Thus, life insurance is a compulsory form of saving for the rainy day. For persons of limited means there is no other alternative substitute of savings.
- Capital Formation : Insurance companies as institutional investors can mobilize small national savings in the form of insurance premia. They usually invest these funds in shares and debentures of business companies and also in government securities. This leads to faster capital formation.
- Insurance offers many benefits to society : Some of the more important services offered by insurance to society in general are :
- It creates confidence among the investing public.
- It ensures security and safety.
- It provides tax relief benefits.
- It encourages provision for the future.
- It leads to higher savings and investments.
- It helps as uncertainty of business losses is reduced.
- It attracts employees of better ability and caliber.
- It enables small businesses to complete with large ones.
- It provides maximum economic growth of the country.
- It creates employment opportunities.
- It ensures larger industrial development.
- It can be used as a measuring rod during the period of inflation and deflation.
Wednesday, August 12, 2009
IMPORTANCE OF INSURANCE

Human beings, his family and properties are always exposed to different kinds of risks. Risk involve the losses. Insurance is a tool which reduces the cost of loss or effect of loss caused by variety of risk. It accumulates funds to meet individual losses. It is not device to prevent unwanted event of happening or cause of loss but protects them against that loss by compensating which as lost. The role and importance of insurance are discussed as follows:
1. Insurance provides security
Insurance provides safety and security against the loss on a particular event. Life insurance provides security against death and old age sufferings. Fire insurance protects against loss due to fire while Marine insurance provides protection and safety against loss of ship and cargo. For personal accident and sickness insurance financial protection is given when the individual is unable to earn. In other insurance too, this security is provided against the loss at a given contingency.
2. Insurance reduces business risk or losses
In Business, commerce and industry, huge properties are employed. Because of slight negligence, the property may be turned in to ashes. A person may not be sure of his life, health and cannot continue the business up to the longer period to support his dependents. By the help of insurance, he can be sure of his earning, because the insurance company will pay a fixed amount at the time of death, damage by fire, theft, accident and other perils.
3. Insurance provides peace of mind
Insurance removes the tensions, fears, anxiety, frustrate or weaken of the human mind associated with the future uncertainty. By providing financial position and promise to compensate losses arise out from various risk, it provides peace of mind and stimulates more and better work performance of an individual.
4. Life insurance encourages saving
The insured has an obligation to pay premium regularly and cannot be withdrawn easily before the expiry of the term of policy. Life insurance encourages the habit of regular and systematic saving through premium and after a certain period, it would be a part of necessary saving of the insured person.
5. Insurance accelerates the economic growth of the country
To develop the economic growth of the country, insurance provides strong hand and mind, with protection against loss of property and capital to produce more wealth. It provides protection against different kinds of loss caused by risk. It accumulates the capital from the insured and utilizes for the development of country. Thus, the insurance meets all the requirements for the economic growth of a country.
6. Insurance provides credit facilities
The insured person can get loan by pledging insurance policy and the interest will not exceed the cash value of policy charged by insurer. In case of death of insured person, the policy can be utilized for setting of the loan with interest. Business person can take loan on the basis of insurance documents from the bank also.
7. Insurance helps to reduce inflation
Inflation created from over supply of money and on less production entities. Insurance can help to reduce the inflationary pressure in two ways. Firstly, it collects money as an amount of premium which controls over supply of money and secondly, it provides sufficient funds for increase production entities. Thus, it reduces the impact of inflation.
8. Insurance makes security and welfare of employees
The security and welfare of employees is the responsibility of employer. These security and welfare are easily met by life insurance, accident and sickness benefit and pension which are generally provided by group insurance. The premium for group insurance is normally paid by the employer. Insurance is the simple method for employer to fulfill their responsibility. Due to these benefits, employee will devote their maximum capacities to complete their job.
9. Other Importances of Insurance
a) Insurance helps to promote foreign trade providing protection again trade risk.
b) Insurance increases business efficiency eliminating the loss of damage, destruction, or disappearance of property of goods.
c) Insurance protects the social wealth providing protection against social evil.
d) Development of insurance business helps to solve the evil of unemployment, generating employment opportunity in the country.
e) The insured gets tax benefit in life insurance.
Search

Unique visiter
| Download a free hit counter here. |
