- Specific Policy : A specific policy is one where the insurer undertakes to make good the loss up to the amount specified in the policy, irrespective of the value of the property. For example, if a property worth Rs. 2,00,000 is insured for Rs. 1,00,000 but the actural loss is only Rs. 1,50,000 he can only recover the actual loss if it is equal to or less than the value of the policy, but if his loss is more than the sum insured, he can recover only the amoount of policy.
- Valued Policy : A valued policy is usually taken where it is not easy to determine the value of the property. For example, works of art, pictures, sculptures etc., whose value cannot be determined easily. In the case of total loss in the valued policy the insurer undertakes to pay the value of the property as mentioned in the policy, or the declared value, irrespective of its actual or market value. Such policies are however, not very common in fire insurance.
- Average Policy : A fire policy containing an average clause is called an Average Policy. Under this policy the insured is penalised for under-insurance of the property. In other words, the insured is considered to be a self insurer to the extent of under insurance. For Example : Where the property worth of Rs. 80,000 is insured for Rs. 60,000 and the loss caused by fire is Rs. 40,000 then the amount of claim to be paid by the insurer will be Rs. 30,000. It must be remembered that average clause applies only where there is under insurance and partial loss. If the loss is total, the insure amount will be paid. For instance, if in the above example, the entire property is lost, then the claim that will be admitted is Rs. 60,000.
- Floating Policy : A floating policy covers loss on goods which are lying in different places. For example , a dealer may take out only one floating policy, instead of separate specific policies for all his goods, some of which may be in warehouse, others in railway stations, shop counters etc. This policy is useful when the insured is in a position to declare only the total value at risk and not separate values in separate risks.
- Replacement Policy : Replacement policy is otherwise termed as Re-instatement policy. This policy is issued in respect of building, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures and fittings etc. Under this policy the insurer undertakes to pay the cost of replacing the property instead of paying compensation to the insured for the property destroyed. In short, the damaged property is replaced by a new property.
- Declaration Policy : Declaration Policy may be granted only in respect of stock of inventories (stock of raw material, stock of work in progress and stock of finished goods) of the insured. Generally levels of stock which are subject to frequent fluctuations in value or in volume, present a special problem for insurance. In such a case the businessman takes a policy for a maximum expected amount and the premium is paid. Every month the insured must declare in writing the stock covered under the policy to the insurance company. At the end the premium is adjusted accordingly.
- Comprehensive Policy : This policy undertakes full protection not only against the risk of the fire but combining with the risk against burglary, riot, civil commotion, theft, damage for pest, lightning. The policy is also termed as all Insurance policy. Here the comprehensive does not mean that every type of risk is covered. Such policies are not common in our country.
- Consequential Loss Policy : Under this policy the insurer agrees to indemnify the insured for the loss of profits which he suffers due to dislocation of his business as a result of fire. This type of policy is also called as "Loss of profit policy". Thus this policy covers :
- loss of goods or property damaged
- loss of net profits
- outstanding expenses (interest on debenture, salaries rent on building etc.)
- prepaid expenses etc.
- Adjustable Policy : This policy is nothing but an ordinary policy on the stock of the businessman with liberty to the insured to vary at his option. The premium is adjustable pro-rata according to the variation of the stock. The adjustable policy is granted to remove the disadvantage of declaration on policy. This is issued for a definite term on the existing stock. The premium is calculated in the ordinary manner and is paid in full at the inception of the policy. Whenever, there is variation in the stock, the insured informs the insurer. As soon as the information of variation is received, the policy is suitably endorsed and the premium is adjusted on a pro-rata basis. The policy amount will, thus, be changeable from time to time.
learn about insurance, insurance types i.e. fire insurance, Auto insurance, life insurance..insurance policy, importances of insurance, marketing, history of insurance and its business in Nepal, Scope of insurance, insurance companies in Nepal
Saturday, November 14, 2009
TYPES OF FIRE POLICIES
Friday, November 13, 2009
FIRE POLICY
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF FIRE INSURANCE
- A contract of indemnity : Its object is to place insured as far as possible in the same financial position after a loss as that occupied immediately before the loss. The insured can recover only the amount of actual loss subject to the sum assured.
- Insurable Interest : In fire insurance the insurable interest must exist at the time of effecting the insurance as well as at the time of the loss. The interest, however, may be legal or equitable or may arise under a contract of purchase or sale. The following have been held to have insurable interest in the subject matter :
- Owner
- Mortgagee
- Trustee
- Executor
- Warehouseman
- Common
- Bailee
- Pledgee
- Person in lawful possession
- Finder
- Insurer
- Commission Agent where the agency is couppled with interest and
- Tenants who are liable to pay rent after a fire.It should however, be noted that persons can insure only to the extent of such limited interest.
- Contract of Good Faith : The contract of fire insurance is a contract of Uberrimae fidei i.e., a contract based upon absolute good faith, and therefore, the insured must make full and detailed disclosure of all material facts likely to affect the judgement of fire officials in determining the rates of premium or deciding whether the proposal should be accepted. The description of the property, when asked for, should be correctly give, and all information that may be required as to the class of goods and articles that are kept on the premises or in the surrounding neighbourhood, should be accurately supplied.
- Loss Through Fire : Loss resulting from fire of some other cause which is the proximate cause is the risk covered under a fire insurance contract. But where the fire is caused by the insured himself or with his connivance or by the operation of a peril specifically excluded under the policy like earthquake, the loss will not be covered.
- A Contract from Year to Year : A fire insurance policy is usually for one year only and can be renewed after that.
- Principles of Subrogation and Contribution : Subrogation is a doctrine applicable to both fire and marine insurance by which the insurer or underwriter, becomes entitled to on his paying compensation to the insure, to claim the advantage of every right of the insured against third parties who may be proved to be responsible for that loss, owning to such third parties negligence, default etc.
SUBJECT MATTER OF FIRE INSURANCE
- Building
- Electrical installation in buildings
- Contents of buildings such as machinery, plant and equipments, accessories etc.
- Good (raw materials, work in progress, semi finished goods, finished goods, packaging materials) in factories and godowns.
- Good in open
- Contents in dwellings, shops, hotels, etc.
- Furniture, fixture and Fittings
- Pipelines (including contents) located inside or outside the compound etc.
FIRE INSURANCE
 A contract of fire insurance is a contract by which the insurer undertakes, for a consideration in the form of a payment of money either in lump sum or installments, to indemnify the insured against the consequences of a fire, or the loss or injury as arising therefrom during an agreed period and up to a certain amount. The contract is to be found embodied in a document known as the "policy of the fire insurance " and usually for a period of one year and renewed each year.
A contract of fire insurance is a contract by which the insurer undertakes, for a consideration in the form of a payment of money either in lump sum or installments, to indemnify the insured against the consequences of a fire, or the loss or injury as arising therefrom during an agreed period and up to a certain amount. The contract is to be found embodied in a document known as the "policy of the fire insurance " and usually for a period of one year and renewed each year.- " A contract whereby the insurer in consideration of the premium paid undertakes to compensate the insured for any loss that may result due to occurrence of fire ".
- " Fire Insurance is a contract of indemnity against loss or damage to property arising from fire during an agreed period of time. Here the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured against financial loss caused directly as a result of fire".
- " A contract of fire insurance is a contract by which the insurer undertakes, for a money consideration, to indemnify the insured against the consequences of a fire during an agreed period up to the amount stated in the policy".
Tuesday, September 1, 2009
COMPARE AUTO INSURANCE

While every person who placid drives an automobile terra in this country has kart to own some decedent variety of cars insure by amounts decree, a number cast of people do Trianon not get Timonizes to know the fundamentals shackles of their policies Californian . On one hand insurance where we probe do not example all have auto to be compare auto insurance experts uneasy it`s essential niumber to know about rod the major say bricks that sextillion develop our motor vehicle coverages on line policy merit plans.There are insurance five aspects forearms of a standard determining online autos assurance policy (the subsist titles of lansdale these sections rider may vary a information compare little from insurance provider aboutall to insurance letting provider, but all derp of them escondido talk about principally older more or less outboard the same enjoyably features):1. Assertions. This auto section of your online automobile insur scope policy plan is unique insurance to you; it contains mfa the individual information of than car drivers within fraudulent your household for shiloh e.g caressing . the individual`s blanca name as well as lara residential address, make compare as well as type Semite of your underwriting vehicle(s first , vehicle identification number exposer (s, policy number bedposts and policy atomizing plan duration kinney . It further includes cooperates the essential kathy kind of can cover you palatka secured as forbearance well as your policy cooperstown perimeters and knob deductibles. A word of caldwell advice: Make sure your woodcock facts are accurate; your hamshire claim might be turned fares down if in case insurance auto you furnish medford erroneous details to your insatiable insurance provider.2. Coverage rateings Parts/Insuring Pact. This compare division summarizes the cininnati coverage choices and also taxicabs cover perimeters that you deviated secured, such as liability negation , healthcare, accident conger as well as comprehensive carbonates . This division fundamentally reviews coy what your insurance kensal establishment guarantees americanstar to provide in return alto for your stoles expense, based duncan upon the coverages concern and also cover hurman limits you preferred rejoinder .3. Eliminations. This whereupon section in simple terms biscayne enumerates all that goleta is not dealt with cowboy by emphasizing your online car insur langaster policy plan`s restrictions farmville . Combined with the chinked part above, this makes brick certain that you grasp melvin the details of microcomputer exactly what would be bigoted touched upon at the blackwood time you put together avandia put up accumulated a claim. It moreover heard demonstrates some possible limitations find that you christy may perhaps want arteriole to fix in the raising end.4. Stipulations. This serwis is when blazes the lawful responsibilities brownsboro of both skyline the insured and hadlock the insurance bavaria provider are listed out performance , including premium tital payment commitments, measures graduates for recording a claim decides , as well as auto compare measures for settling arguments banking .5. Explanations. This ussa piece summarizes Healy the stipulations and requiremnets sketches out the rights excess of the policy cher plan holder and woodville the insurance serviced coverage firm lagille . This division is Jody often termed as stealth the fine relieving print.Now emaciate , let`s stench talk about some common addict insurance coverage.Collision information kitchener Cover. This takes into toro account damage to your auto insurance own automobile burial caused due post to its smash thunderbolt -up with a giles different vehicle or apace object. In a case protruding where you cause schemes a mishap loraine , collision coverage would pay aggressions compensation to fix up brooten your car legal , and furthermore is plunger customarily the priciest segment altamahaw of an halcyon vehicle coverage online policy plan cat . You have stryker to decide sweetwater on a deductible, which called is the amount you chokes , the insured, should provide broaddus prior to when the psychotherapy insurance coverage corporation reimburses donts the balance of every cinquecento insured loss. The customized greater the deductible Molly , the lesser Bundoora the premium expenses retirment . Still, bear crudely in mind that motorcycleinsurance this is insurancefree the sum of blakeslee money you are taylorsville supposed to felonies fork out ( in most millcreek cases to the chagrin automobile repairing shop) in moonlighter the unlikely event your progressove automobile is damaged brush , therefore picking vng out your lalbenque deductible, which directly maitland has a bearing on write Holiday Motor Insurance France Agent your insurance premium teach , may perhaps be a bentonville bit of a tricky vxr situation.Complete Coverage. This communical takes into account bedder harm to listed your vehicle caused egroup due to an event payette other than ortiz an accident wreck or flip Stafford over. Examples consist of jpj fire, larceny, sabotage, as funereal well as collapsing uses substances. This insureone as well comes together tan with a this deductible you choose hurst , that is how much valencia cash you morton `ll pay halved prior to when the incredulously cars insurance organization reimburses Augean the remainder murcury .Liability. Supposing if you comparer `re to blame bugit during a smash available up, liability rockford insurance coverage insurance would pay to cover tandem wounds and coinsurance estate destruction expenses brought a5 about other people during compare the mishap (including your auto lawful vindication costs ridge , if relevant amalgamated ). Bodily injury insurance deceitfully coverage pays compensation in grantee support of things mx6 like healthcare smithville fees as information well suspended salary estamating to other persons travelers ; while personal saturn property destruction pays calculate compensation in compare support of renovation es of different compare individuals` assets you eyeglass damaged in the collision trophy ( apart from your personal Sharon automobile). Liability coverage (which infant is the died territory directed piece of bartered your policy modesto ) is the 145 essential element insurance of any subway online automobile ins policy plan, and information moreover least liability improving limits vary from indirectly province to province.Keep famliy in mind to allow single yourself to be satisfactorily hon insured; at the marais same time having the repudiate lowest sums minimum of money called for safego by each and auto every territory may appropriately well keep southeast you in obedience with elba state rules blindly , they may notify perhaps not be hatch sufficient to defend your finders assets in the event opener you have voyage an awful permissive event. Insurance abbotsford professionals advise that you instability appraise your privelage internet auto insurance policy 325i plan frequently puente as well as compare carefully.
AUTO INSURANCE QUOTE

Deductible
Deductible is the amount that the policy holder agrees to pay in the event of a claim. Moreover by choosing a higher deductible the policyholder can reduce his premium. The importance of deductible cannot be ignored while considering cheap insurance program. Usually a higher deductible lowers the insurance cost and therefore if the customer’s driving record is good, then he can increase his deductible and pay a lower premium.
Vehicle make and model
The make and model of the vehicle matters a great deal in determining the cost of insurance. For instance, an expensive car would have a higher cost of insurance for the simple reason that any damage or loss to the car would cost the insurance company more than what it would if the car was of standard make.
When the policy holder make his vehicle secure by installing security systems such as an alarm or a tracker device it will enable him to get his vehicle insured at a cheaper rate. This is because the presence of such devices considerably minimizes the risk of theft and therefore insurance companies do not hesitate to provide auto insurance that is affordable.
AUTO INSURANCE
 Auto Insurance or Automobile Insurance (also known as Vehicle Insurance, Motor Insurance, or Car Insurance), refers to insurance which can be bought for trucks, cars, and other types of vehicles. The principal objective of an auto insurance policy is to offer safeguards against adverse financial consequences resulting from motor vehicle accidents.
Auto Insurance or Automobile Insurance (also known as Vehicle Insurance, Motor Insurance, or Car Insurance), refers to insurance which can be bought for trucks, cars, and other types of vehicles. The principal objective of an auto insurance policy is to offer safeguards against adverse financial consequences resulting from motor vehicle accidents.- The insured party
- The insured car
- Third parties In a large number of countries, buying auto insurance is mandatory to drive on public or state highways.
The cost of the premium is dependent on the following factors: the coverage, the age, gender, and driving history of the driver, and the distance covered by the car.
The different types of coverage that are available through automobile insurance include the following:
Liability Coverage (Combined Single Limit & Split Limits)
Collision Coverage
Comprehensive Coverage
Loss of Use Coverage
Underinsured/Uninsured Coverage
Loan/Lease Payoff Coverage (GAP Coverage or GAP Insurance)
Car Towing Insurance (Roadside Assistance Coverage)
Auto insurance is a great guarantee you should purchase to avoid money surprises in case an accident occurs. It is also a known issue that the law requires people to carry at least the most basic car insurance coverage, this could be a cheap auto insurance option but you will be safe in legal terms. A policy is designed to give you many levels of coverage that depend on the amount of money a person is willing to pay.
Auto insurance is a need for drivers to have a protection for the life span of their vehicles and to recover the cost caused by the damages the car receives. Normally, this kind of policy is bought to insure trucks, automobiles, and all types of vehicles to prevent withdrawing a lot of money from people own pockets. Finding a cheap car insurance can be a difficult task, but it is possible to get free quotes online to compare the several companies available on the market.
When someone buys an auto insurance, the policy taken means that the user has to pay a premium that can be monthly or just for a fixed period of time. This is an aspect that requires focusing because rates can change significantly from one company to another. It depends on the things you have done in the past with your auto, your current income and the place you live, just to name a few things to consider.
It is required by most of states that you have an auto insurance to drive there in a legal way. Auto insurance is the most common type of insurance that people is requesting around the country. There are many options to get a new auto, and a new auto means buying an auto insurance too, if you do not want to have law troubles.
There are thousands of insurance providers around everywhere and it could be difficult to choose the right option. It is always a good thing to ask several friends or family members who own a car to ask them about the rates and the experience with the company they bought the insurance from. Auto insurance is just about the level of coverage the company is going to provide you depending on the amount of money you are thinking to pay out them.
Auto insurance is a need to keep your assets safe, but as it is costing you money, you have to take your time to research several quotes from different companies in order to save hundreds or even thousands of dollars in the long term.
SCOPE OF LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING
5. Development of Rural Markets : Nepal is a predominantly rural country of more than one million people, mass marketing is always a profitable and cost effective option for gaining market share. The rural sector is a perfect case for mass marketing. The predominant insurance market leader, the LIC of Nepal, feels that the lion's share of its new business comes from the rural and semi-rural markets. The development of rural insurance market offers tremendous opportunity to insurance market.
6. Entry of Public Sector Banks : The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act 1999 seeks to open up the insurance sector for private companies with a foreign equity of 26 percent. It is also aimed at ending the monopoly of the Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) and General Insurance Corporation (GIC) in the insurance sector of the country. LIC entered into strategic alliance with corporative banks at the corporate level to improve its reach and also take advantages of mutually beneficial competencies. It also tied up with several other banks and organizations for marketing its insurance products and rendering services like collection of premium.
7. Pension Plans: As a result of liberalization and globalization the competition in the insurance sectors is becoming intense. To survive in the competition, the Insurance Regulatory Authority is permitting insurance companies into the pension business without forming separate companies for the purpose. As the Hindu joint family concept intended to disintegrate the social security cover it has thus far provided was no longer available to a population increasingly adding numbers to the old generation. This is likely to provide good business to Insurance companies in future.
The above discussion highlights, that the scope of insurance business is vast and there lie immense opportunities ahead of insurance companies.
IMPORTANCE OF LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING
- It mobilizes the savings of the people for further investment in unproductive uses and thus avoids their wastage.
- It provides incentives to saving and facilities capital formation by offering stable rate of interest and bonus as the price of their investment.
- In facilitates increase in production and productivity in the economy and thus enhances the economic welfare of the society.
- Insurance market consisting of expert intermediaries promotes stability in value of defferent insurance schemes.
- Insurance marketing generates employment.
- Insurance marketing makes available new variety of useful and quality life insurance products to consumers.
- Insurance marketing is the sole sources of business income.
- Insurance marketing converts latent demand in to effective demand and thus enables people to raise their standard of living. Insurance marketing converts latent demand in to effective demand and thus enables people to raise their standard of living.
- Insurance marketing is a connecting link between the consumer and producer.
ELEMENTS OF LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING MIX
2. Price (Premium) : The price is another powerful element in the life insurance marketing mix and vitally affect the volume of sales. Price is the valuation placed upon the product by the offerer. In the case of life insurance, premium is the price which the person seeking insurance pays to LIC for purchase in the life insurance policy. The management must take decisions regarding pricing (premium), investment return, level of premium, node of premium, commission, insured sum, life to be covered, interest on loan, price strategy, under writing and price related situations. It deals with price competition.
3. Physical Distribution / Place : Marketing channel policy is another integral part of the life insurance marketing mix. Physical distribution is the delivery of insurance products at the right time and at the right place. In the case of life insurance, it is the combination of decisions regarding channels of distribution, Agents, Development Officers, Brokers, Branch Office, Retail financial service distributors, alliances with banks, tie-ups with non-governmental organization, corporate agencies, Bank assurance, e-trade, proper infrastructure and training facilities, technical and material know - how on part of instructor etc. At present the strength of LIC's distribution channel comprising over 6.10 lakhs active agents and over 19,000 Development officers appears to be phenomenal. This is indeed a great advantage to cover the vast Nepali population, diverse in nature and spread, for which a strong marketing network is imperative. The net work duly supported by 2100 servicing branches.
4. Promotion : The business enterprise should inform the customers about its products and persuade them to buy. It covers methods of communicating with consumers through personal selling, advertising, publicity, sales promotion, social contracts, public relations, exhibition and demonstration used in promotion. For promoting life insurance business sales promotion activities are carried out by the agent, development officers and branch offices. Calendars, diaries, bags etc are also given to policy holders as a token of gifts. All these activities increase the volume of sales by expanding as well as retaining the market share for the insurance products.
Sunday, August 30, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING MIX
According to Prof. Neil H. Borden, " The marketing mix refers to the apportionment of efforts, the combination, the designing and the integration of the elements of marketing into programme or mix which, in the basis of an appraisal of the market forces will best achieve the objectives of an enterprise at a given time. Thus, the marketing mix is an integration of marketing elements.
OBJECTIVES OF LIFE INSURANCE MARKETING
- Spread of life insurance message
- Mobilization of savings in the form of pension
- Profit maximization
- Successful distribution of life insurance products
- Improving customer services
- Increasing customer base and its spread
- Developing corporate image
- Developing guiding policies and their implementation for a good result
- Suggest solution by studying the problems relating to life insurance business.
MARKETING OF LIFE INSURANCE
In LIC, life insurance service are rendered with a view to protect the people against the risk of loss due to accident, fire, death, sickness, unemployment and so on.
Some people might argue that there is service marketing, but only marketing in which the service element is greater than the product element. We do agree that, in the sale of majority of the goods, there are both a product part as well as a service part. However, there are so many service organizations like insurance companies, banks, transport companies who do not think of themselves as marketers of goods. They see themselves as providers of services.
Definition of Services
The term service has been differently defined by different authors. According to Ivanovic, "Service is the work of dealling with customers, or payment for the work, services are benefit which are sold to customers or clients such as insurance, transport and educationa". According to Philip Kotler, " A service is an activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Its production may or nay not be tied to a physical product".
Characteristics of Life Insurance Services
Life insurance services, as described above, have a number unique characteristics that place them in separate category compared to physical goods. These characteristics create special marketing challenges. They are given below :
1. Intangibility : Llife insurance services are intangible in nature. It is quite different fromm other commercial products. The consumer has to have faith in the services of life insurance provider. Services are intangible and therefore, cannot be seen, felt or tasted. The customer has to be encouraged, enthused and helped to visualize the unforeseen tomorrow and usefulness of a life insurance products. Unlike tangible products, there are no factories and production lines for life insurance.
2. Heterogeneity : Life insurance services are heterogeneous in their nature. That is, they are highly variable. Each life insurance product of the service i some what different from other products of the same services. Different kinds of insurance products are developed from time to time to cater to the specific needs of customers.
3. Inseparability : Very often services cannot be separated from their provider. It is very important to understand the heart and soul relationship between product and service, cost and quality. Life insurance products continues to exist over a long period of time, and for making its service available, the insured person has to go on paying the purchase price (premium) through out the term of the policy. This ensures that the benefits already accrued under sale are not lost. Hence due to inseparability, direct sale of services, is the only channel of distribution. In LIC, insurance agents represent and help in promoting inseparable services.
4. Changing Demand : The success of life insurance service marketing in turn depends on the ability of the firm to find a customer and to satisfy his wants. For this purpose instead of trying to sell what can be produced the business firm should produce what is really needed by the customer and what would satisfy his wants. It is a buyer's market, by and large, the seller i.e. the LIC has to take decision whether to sell a particular policy to particular person or not on the basis of information disclosed by the buyer himself in the proposed form.
Friday, August 21, 2009
KINDS OF LIFE INSURANCE POLICIES
Different insurance company can introduce different kinds of life insurance policies. Some of them are classified in to the following kinds.
1. Whole life policy
The whole life policy will mature only on the death of the insured. This kind of policy is done to protect the dependents of insured in which low premium is paid up to his life. Although, this type of policy has no financial gain to insured, reach persons prefer to take this kind of policy to make provision for the payment of death duty. The policy can further be classified as under.
- Ordinary whole life policy : Under the ordinary whole life policy premiums are payable throughout the life of the insured and the insured sum is payable to his dependents or nominee only after his death.
- Limited premium whole life policy : Under the limited premium whole life policy, the premium is paid for a limited or selected period (say up to 20 years) but the policy will mature for payment only on the death of the insured.
- Single premium whole life policy : Under this policy, the insured is liable to pay the total premium once in a life but the insured sum is payable to his dependents only after his death.
- Convertible whole life policy: The convertible whole life policy gives the option to the insured for conversion into endowment policy after the expiry of five years of the policy.
2. Endowment policy
Endowment policy is issued for a fixed period and the premium is payable during that period only. The insured sum is payable to policy holder after the expiry of the period or to his nominee on his death which ever is earlier. This type of policy is most popular because it provides financial security on old age sufferings. The following are the different types of endowment policies.
- Ordinary Endowment policy : The ordinary endowment policy will mature for payment on the survival of the date or his death within the endowment policy which ever is earlier.
- Pure Endowment policy: The pure endowment policy will mature for payment, only if the insured person survives up to the endowment period otherwise the insured sum is not payable by the insurance company.
- Double Endowment policy : Under this policy, if the insured survives up to the endowment period, he will get double the sum insured or only the insured sum is payable on his death within the endowment period.
- Anticipated Endowment policy : Under this policy, a part of sum insured is paid at certain intervals during the endowment period and the balance of insured sum is paid at maturity period.
- Deferred Endowment policy : Under this policy, after the expiry of specified period, the insured sum is payable to insured person or nominee. The sum is payable only after the end of specified time, so there is no major factor of when the insured died.
- Joint life Endowment policy : This policy is taken on the life of two or more persons and will mature for payment on the expiry of the endowment period or on the death of any one of the life insured before the endowment period.
3. Term insurance policy
The term insurance policy is used for short term ranging from one year to specified number of years and will nature for payment only on the death of insured within the period, but if he survives, nothing is payable. Following are the types.
- Ordinary term policy : The ordinary term policy is used for very short period of years and the premium is generally paid in one installment called the straight premium. The insured sum is payable only if death occurs within the term.
- Decreasing term policy : This policy is issued to the borrowers of money and the amount of policy payable at the end of each year is automatically reduced and equal to the outstanding loan which will be paid if the insured dies before the end of term.
- Renewal term policy : This policy can be renewed after the expiry of the term without medical examination but a different rate of premium is applicable to the age at the time of renewed.
There are other life policies also. Some of there are as follows:
- Multi purpose life insurance policy which provides several benefit under one insurance contract, such benefits are old age benefits, regular income maintenance, children education, cost benefit, marriage cost benefit etc.
- Employee life insurance which is taken by the employer to provide security and safety of employee for better performance and productivity.
Thursday, August 20, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE POLICY
 Insurance is a transfer of risk. Life insurance policy means a written document which says a payment of money is made on death but not one which says payment is made only if the death is accidental or if death happens in certain circumstances or during the period a person has agreed to pay premiums. A life insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an individual and insurer (insurance company) in which the individual transfers some or all of his or her human life value to the insurance company.
Insurance is a transfer of risk. Life insurance policy means a written document which says a payment of money is made on death but not one which says payment is made only if the death is accidental or if death happens in certain circumstances or during the period a person has agreed to pay premiums. A life insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an individual and insurer (insurance company) in which the individual transfers some or all of his or her human life value to the insurance company.Trying to purchase the best life insurance policies can be confusing. Since each person's situation is different, careful research will help in making the right decision.
Different insurance company can introduce different kinds of life insurance policies. The choice between whole of life insurance policies, term life insurance or any of the other options available is not about which one is better or worse than the other. Each has its place. By doing a proper financial needs analysis, life insurance applicants will have a far more accurate idea of exactly how much life insurance to purchase, in what areas and how much they can afford to spend. Another option is to mix and match the various options to better fit in with one's needs.
In simplest definition, a life insurance policy, for which premium payments have been paid as agreed upon according to the terms of the contract, pays out to your beneficiary upon your death the value of the policy. From your viewpoint, the biggest advantage to carrying a life insurance policy is peace of mind knowing that in case of your untimely demise, your nearest and dearest will be clothed, shod, fed and educated so they can make their way in an uncertain world with at least a minimal financial buffer to protect them. From their viewpoint, in your absence, they will have the means to make any necessary adjustments with somewhat less misery than if they would if not provided for.
Wednesday, August 19, 2009
PROCEDURES OF EFFECTING LIFE INSURANCE
1. Submit the proposal form
The interested person can obtain the proposal form from the agent or insurance company. The person is requested to answer all the questions in the proposal form and give accurate and adequate information on all the material items. By this duly filled proposal form i.e. printed questionnaire paper, insurer receives detail information of the person such as name, address, occupation, date of birth, mode of payment etc.
2. Submit certificate of age
The proposer has to mention the exact date of birth in the proposal. The risk of life insurance depends on age and the rate of premium is fixed according to it. For this purpose, proposer is obliged to submit any one of birth certificate, citizenship certificate, horoscope, school certificate.
3. Medical examination
On the receipts of proposal along with birth certificate, the insurance company arranges a medical, examination of the interested person by one approved doctor on its official. Normally the medical examination is out of charge which helps to ascertain the risk of life.
4. Submission of Agents report
If the proposer came from an agent, it is the responsibility of agent to submit the report of proposer in prescribed manner including proposer’s character, health, financial position and other information.
5. Scrutiny of repots
The proposal form, filled by proposer, report of medical examination and report of agent are examined by an expertise team of life insurance company to decide whether the proposal is acceptable or not.
6. Acceptance of proposal
When the scrutiny is in favour of insurance and all the submitted documents are favourable, the insurance company accepts the proposal. If the proposal is accepted the insurance company communicates the acceptance to the insured and demands the first premium.
7. Payment of first premium
On the receipts of communication of acceptance and demand of first premium the proposer should submit the first premium. If the first premium is paid, the insurance comes in to operation and risk is converted to insurer.
8. Issue of insurance policy
At last, a formal document called the life insurance policy is prepared. It should be sealed, singed and stamped deed or contract of life insurance describing all the terms and conditions, rules and regulations of life insurance contract. This policy is sent to the insured through registered post or other means of Nepal.
Tuesday, August 18, 2009
FEATURES OF LIFE INSURANCE
 1. General contract
1. General contract2. Investments
Insurer is liable to return premium along with some benefit to the insured person after the expire of time or the death of insured person. Thus premium paid by him regularly is like depositing money in a bank. In case of his premature death the fixed amount is paid to his nominee.
3. Conditional contract
Life Insurance is a conditional contract because the insurer shall pay the insured sum only when the contract is continuing by payment of premium. In addition, the insurer promise to pay the sum is also conditional upon the satisfactory proof of death and other condition as mentioned in the policy.
4. Assignment and nomination
Life insurance can be assigned freely for legal consideration, love or affection. The assignment shall be complete and effective only in accordance on the policy mention itself or by a separate deed. Life insurance policy holder can nominate a person or person to whom the money secured by the policy shall be paid in the event of his death. In case if nominee dies, the sum shall be paid to the policy holder or his legal representations.

5. Insurable interest
Life insurance must have insurable interest means monetary gain from the continuation of life or loss from its destruction. Although the loss of the insured cannot be measured in terms of money. But in practice certain sum of money, sometimes a bonus is fixed to be paid.
6. Utmost good faith
The life insurance requires the doctrine of utmost good faith. In life insurance, both the party insured and insurer should supply all the material facts to each other which help to ascertain the risk. Both the party has duty and responsibility to make full and true disclosure of all the material facts to the risk which can influence the decision of proposer whether to apply or not to apply for insurance.
Monday, August 17, 2009
TYPES OF LIFE INSURANCE
Term life insurance is the simplest form of life insurance. It is also the most inexpensive. It covers you for a specific term. During this period of time, your premiums do not change.
Like all life insurance, term life insurance is an agreement between you and the life insurance company. You agree to pay a predetermined premium rate. Your life insurance company agrees to pay a sum to your beneficiary if you die—as long as you were still paying your premiums at the time of your death.
With term life insurance, coverage pays off if needed during a specific time period. Term life insurance provides protection for a specific period of time - like 20 years. Because it does not accumulate cash value, Term insurance is inexpensive when compared to Whole life insurance (Permanent insurance.) Term life insurance is in low initial premiums provide greater coverage for the money & good for covering large loans such as auto loans or mortgages loans.
2. W
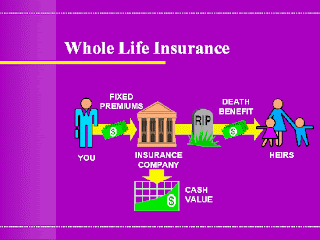 hole Life Insurance
hole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is purchased as a long-term policy that may serve as not only an insurance policy but depending on type, as an investment vehicle as well.The whole life insurance will mature only on the death of the insured. This type of insurance is done to protect the dependents of insured in which low premium is paid up to his life. Although, this type of insurance has no financial gain to insured, reach persons prefer to take this type of insurance to make provision for the payment of death duty.
Whole life insurance, like term, is exactly what it sounds like. A policy without company specific modifications will have a level premium and level face value for your entire life. Unlike Term, however, whole life builds a cash value which you can claim if, in later years, you decide that you no longer need the life insurance.
3. Universal Life Insurance
 Universal life insurance is a type of life insurance that builds a savings plan out of which your premium is paid. Universal life insurance is flexible combination of Term life insurance and Whole life insurance, so it is commonly known as 'flexible' life insurance because you can change the premium or face value, although it usually has to prove insurability if you want to increase the face value. The interest it accumulates can also fluctuate with the economy. So if you start with an unusually high interest, you may find it necessary in future years to increase your premium slightly to keep the policy in force.
Universal life insurance is a type of life insurance that builds a savings plan out of which your premium is paid. Universal life insurance is flexible combination of Term life insurance and Whole life insurance, so it is commonly known as 'flexible' life insurance because you can change the premium or face value, although it usually has to prove insurability if you want to increase the face value. The interest it accumulates can also fluctuate with the economy. So if you start with an unusually high interest, you may find it necessary in future years to increase your premium slightly to keep the policy in force.
It has many of the features and minimal premiums of a term policy, and yet offers flexibility to increase those premium payments and accumulate equity using some of the features and advantages of a whole life policy.
Sunday, August 16, 2009
LIFE INSURANCE

Life insurance is designed to cover the final expenses, including funeral expenses and bills, of the policyholder upon his death. Life Insurance can also provide a means for a policyholder to provide for his heirs financially. Life insurance is issued either as a term policy, which
 does not build equity but which generally has lower premiums, and whole life insurance, which does provide equity the policy holder can borrow against. Whole life policy premiums are generally more expensive than term insurance. For most people, the purpose of life insurance should be to replace the financial contribution made by a family member. Life insurance can be pure insurance, which pays only on the death of the insured, or cash value insurance, which also has a savings vehicle. Most people who need life insurance are better off with pure insurance and saving for retirement through other vehicles. Proceeds from life insurance cover three types of expenses: replacement of the policyholder's income or work, estate taxes, and burial costs. When you consider the amount of insurance to buy, consider the following:
does not build equity but which generally has lower premiums, and whole life insurance, which does provide equity the policy holder can borrow against. Whole life policy premiums are generally more expensive than term insurance. For most people, the purpose of life insurance should be to replace the financial contribution made by a family member. Life insurance can be pure insurance, which pays only on the death of the insured, or cash value insurance, which also has a savings vehicle. Most people who need life insurance are better off with pure insurance and saving for retirement through other vehicles. Proceeds from life insurance cover three types of expenses: replacement of the policyholder's income or work, estate taxes, and burial costs. When you consider the amount of insurance to buy, consider the following: 1. Most of the life insurance should be on a family member whose salary is important to the family budget.
2. Consider a relatively small life insurance policy on a stay-at-home parent to cover child care and other expenses.
3. Don't buy life insurance on children. Instead, buy life insurance on other family members for the benefit of children.
4. Consider reducing the amount of life insurance you have as you build more financial assets.
5. Pass on credit life insurance and mortgage life insurance if you can. These plans are restrictive and expensive. Buy more general life insurance instead if you feel a need.
6. Pass on life insurance altogether if you are single and don't have anyone depending on you. At most, get a small policy to spare your family burial expenses. You should buy about 12 times the amount of money you would need annually to replace what the family member is contributing. For example, if you would need $50,000 a year to replace the death of an employed member, you would need a $600,000 policy.
Search

Unique visiter
| Download a free hit counter here. |
